- Bitcoin Price Prediction 2025: Decoding The Future Of The Crypto King
- How Does Bitcoin Work? A Deep Dive Into The Cryptocurrency Revolution
- Bitcoin Mining: A Comprehensive Guide
- Bitcoin Mining Rigs For Sale: A Comprehensive Guide
- How To Buy Bitcoin: A Comprehensive Guide For Beginners And Beyond
Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has revolutionized the financial landscape with its decentralized and secure digital currency system. However, the energy-intensive process of Bitcoin mining has raised concerns about its environmental impact. This article delves into the energy consumption of Bitcoin mining, exploring the factors that contribute to its high energy usage, the environmental consequences, and potential solutions for a more sustainable future.
Understanding Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is the backbone of the Bitcoin network, responsible for verifying and adding new transactions to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, competing to add the next block to the blockchain. The first miner to solve the problem is rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins and transaction fees.
The mining process requires specialized hardware, such as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), which are designed to perform the complex calculations efficiently. These ASICs consume significant amounts of electricity, contributing to the high energy consumption of Bitcoin mining.
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption
Several factors influence the energy consumption of Bitcoin mining:
-
Mining Hardware: The type of mining hardware used significantly impacts energy consumption. ASICs are more energy-efficient than CPUs and GPUs, but they still consume substantial amounts of electricity.
-
Mining Difficulty: The Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of the mining problem to maintain a consistent block creation rate. As more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, requiring more computing power and energy to solve the problem.
-
Electricity Costs: Miners tend to locate their operations in regions with low electricity costs to maximize their profitability. This can lead to the concentration of mining activities in areas with cheap but potentially polluting energy sources.
-
Mining Pool Participation: Miners often join mining pools to increase their chances of earning rewards. Mining pools coordinate the efforts of multiple miners, pooling their computing power and sharing the rewards.
Bitcoin Price: The price of Bitcoin influences the profitability of mining. When the price of Bitcoin is high, miners are more incentivized to invest in more powerful hardware and consume more energy to mine more Bitcoins.
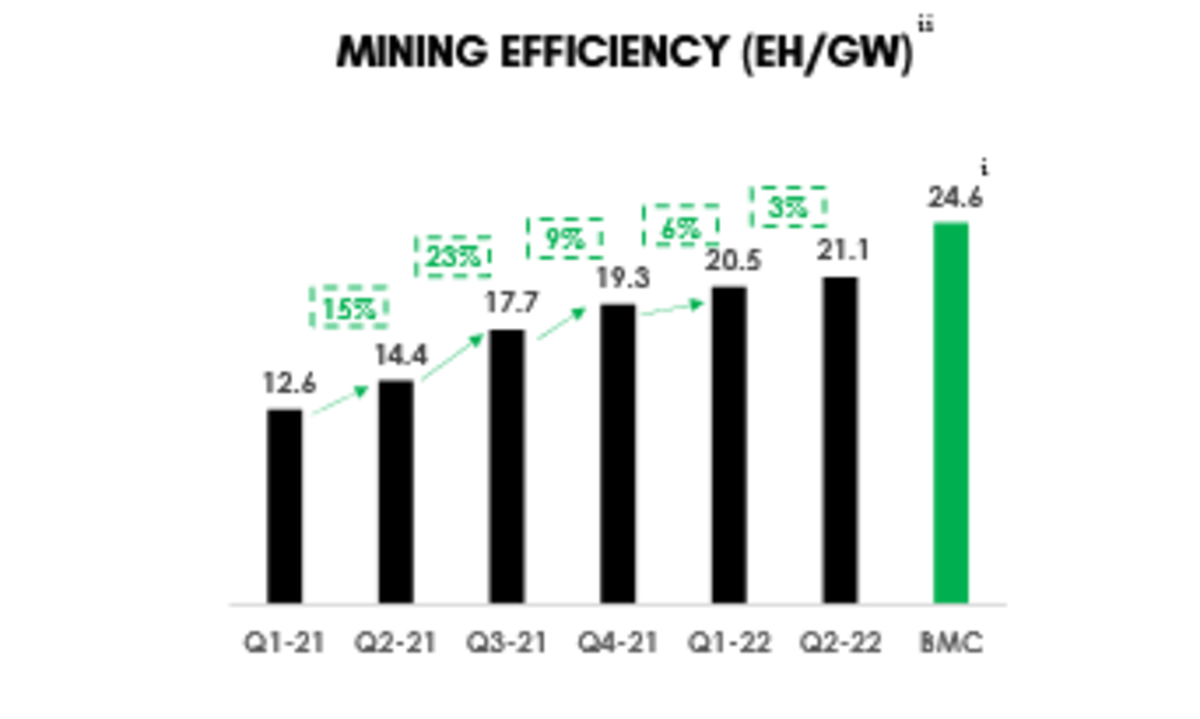
Estimating Bitcoin’s Energy Consumption
Estimating the energy consumption of Bitcoin mining is a complex task due to the decentralized and opaque nature of the network. However, various organizations and researchers have attempted to estimate Bitcoin’s energy usage using different methodologies.
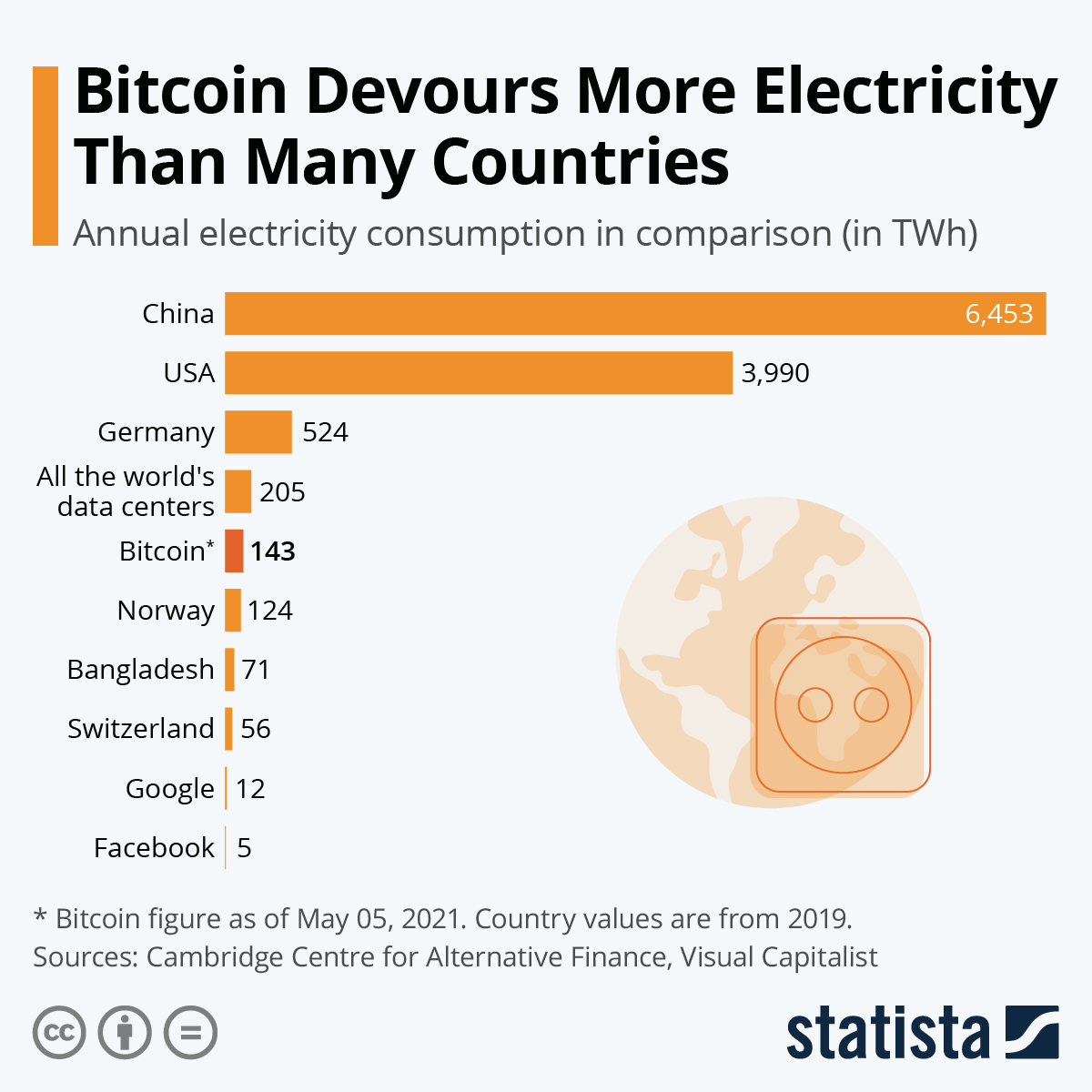
The Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index (CBECI) is one of the most widely cited sources for estimating Bitcoin’s energy consumption. CBECI uses a model based on the energy efficiency of mining hardware and the Bitcoin network’s hashrate to estimate the total electricity consumption of Bitcoin mining.
According to CBECI, Bitcoin’s annualized electricity consumption is estimated to be around 121 terawatt-hours (TWh) as of November 2023. This is comparable to the annual electricity consumption of countries like Argentina or the Netherlands.
Environmental Consequences
The high energy consumption of Bitcoin mining has significant environmental consequences:
-
Carbon Emissions: A significant portion of Bitcoin mining is powered by fossil fuels, particularly coal, leading to substantial carbon emissions. These emissions contribute to climate change and air pollution.
-
E-Waste Generation: Bitcoin mining hardware becomes obsolete quickly due to technological advancements and increasing mining difficulty. This results in a large amount of electronic waste (e-waste), which contains hazardous materials and poses environmental risks.
-
Resource Depletion: The production of mining hardware requires significant amounts of resources, including rare earth minerals. The extraction and processing of these resources can have detrimental environmental impacts.
-
Noise Pollution: Bitcoin mining operations can generate significant noise pollution, especially in areas with large-scale mining farms.
Efforts Towards Sustainable Bitcoin Mining
Recognizing the environmental concerns associated with Bitcoin mining, various initiatives are underway to promote more sustainable practices:
-
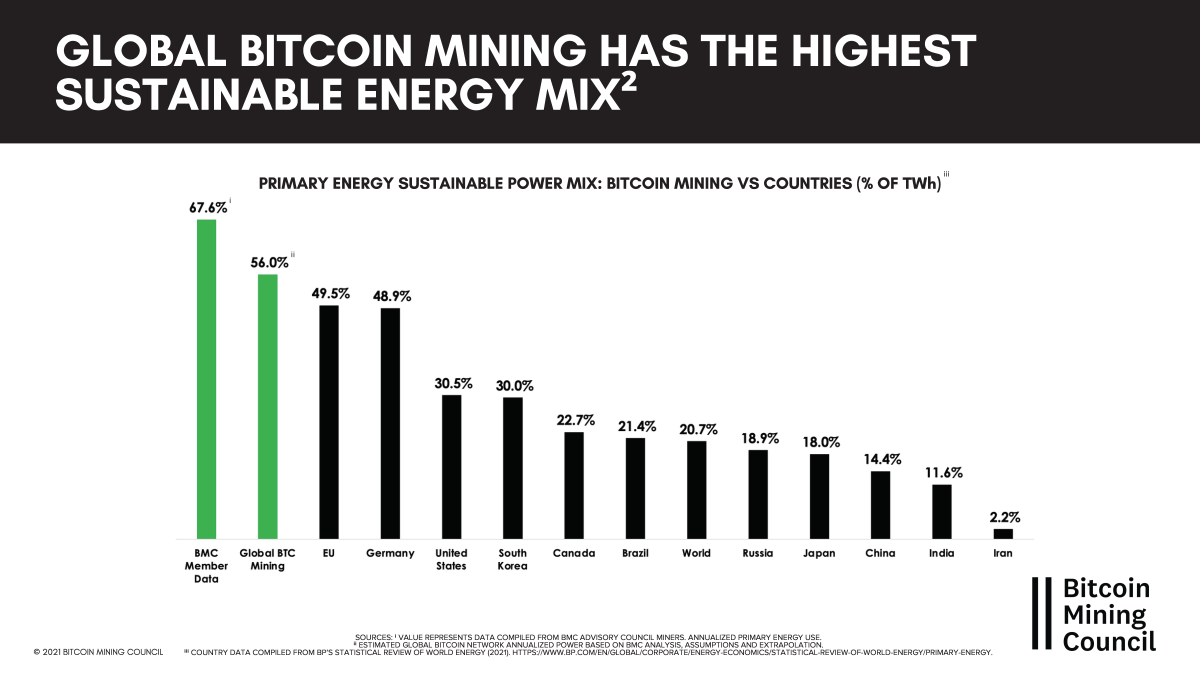
Renewable Energy Adoption: Miners are increasingly turning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power, to power their operations. This reduces the carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining and promotes the transition to a cleaner energy system.
-
Energy Efficiency Improvements: Manufacturers are developing more energy-efficient mining hardware, reducing the amount of electricity required to perform the same amount of mining.
-
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Consensus Mechanism: Some cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum, have transitioned to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which is significantly more energy-efficient than Proof-of-Work (PoW). PoS eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining and replaces it with a system where validators stake their cryptocurrency to validate transactions.
-
Carbon Offsetting: Some Bitcoin mining companies are investing in carbon offsetting projects to compensate for their carbon emissions. These projects include reforestation, renewable energy development, and carbon capture technologies.
-
Regulatory Measures: Governments and regulatory bodies are exploring measures to regulate Bitcoin mining and promote more sustainable practices. These measures include carbon taxes, energy efficiency standards, and incentives for renewable energy adoption.
The Future of Bitcoin Mining
The future of Bitcoin mining is likely to be shaped by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory developments, and market forces. As renewable energy becomes more affordable and accessible, miners are likely to increasingly adopt renewable energy sources to power their operations.
Energy-efficient mining hardware will also play a crucial role in reducing the energy consumption of Bitcoin mining. As manufacturers develop more efficient ASICs, the overall energy footprint of the Bitcoin network will decrease.
Regulatory measures, such as carbon taxes and energy efficiency standards, could also incentivize miners to adopt more sustainable practices. These measures could make it more expensive to operate using fossil fuels and encourage the use of renewable energy.
The transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms could also significantly reduce the energy consumption of cryptocurrencies. While Bitcoin is unlikely to transition to PoS in the near future, other cryptocurrencies are exploring this option as a way to reduce their environmental impact.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining’s high energy consumption is a significant environmental concern. The process requires specialized hardware and electricity, contributing to carbon emissions, e-waste generation, and resource depletion. However, efforts are underway to promote more sustainable practices, including renewable energy adoption, energy efficiency improvements, and carbon offsetting. The future of Bitcoin mining is likely to be shaped by technological advancements, regulatory developments, and market forces, with a focus on reducing its environmental impact. As the world transitions to a more sustainable energy system, Bitcoin mining must adapt to ensure its long-term viability and minimize its environmental footprint.

