- Bitcoin Tax Implications: A Comprehensive Guide For Cryptocurrency Users
- Bitcoin Market Cap In 2025: A Deep Dive Into Potential Scenarios
- How To Store Bitcoin Securely: A Comprehensive Guide
- Bitcoin Mining Profitability: A Comprehensive Guide
- What Is Bitcoin Halving? A Deep Dive Into The Crypto Event
Bitcoin, the world’s first and most well-known cryptocurrency, has revolutionized the financial landscape. However, as its popularity has grown, so have concerns about its scalability. The Bitcoin network can only process a limited number of transactions per second, leading to slow transaction times and high fees, especially during periods of high demand. This is where the Lightning Network comes in.
The Lightning Network is a layer-2 scaling solution built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain. It aims to solve Bitcoin’s scalability issues by enabling faster, cheaper, and more private transactions. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of the Lightning Network, exploring how it works, its benefits, and its potential impact on the future of Bitcoin.
The Scalability Challenge of Bitcoin
Before understanding the Lightning Network, it’s crucial to understand the challenges Bitcoin faces. The Bitcoin blockchain operates on a decentralized, peer-to-peer network, where every transaction must be verified by multiple nodes. This verification process, known as mining, consumes significant computational power and time.
The Bitcoin blockchain has a block size limit of 1 megabyte, and new blocks are added approximately every 10 minutes. This limits the number of transactions that can be processed per second to around 7. As the demand for Bitcoin transactions increases, the network becomes congested, leading to longer confirmation times and higher transaction fees.
This scalability problem has hindered Bitcoin’s adoption as a mainstream payment method. For Bitcoin to become a viable alternative to traditional payment systems, it needs to handle a much larger volume of transactions quickly and affordably.
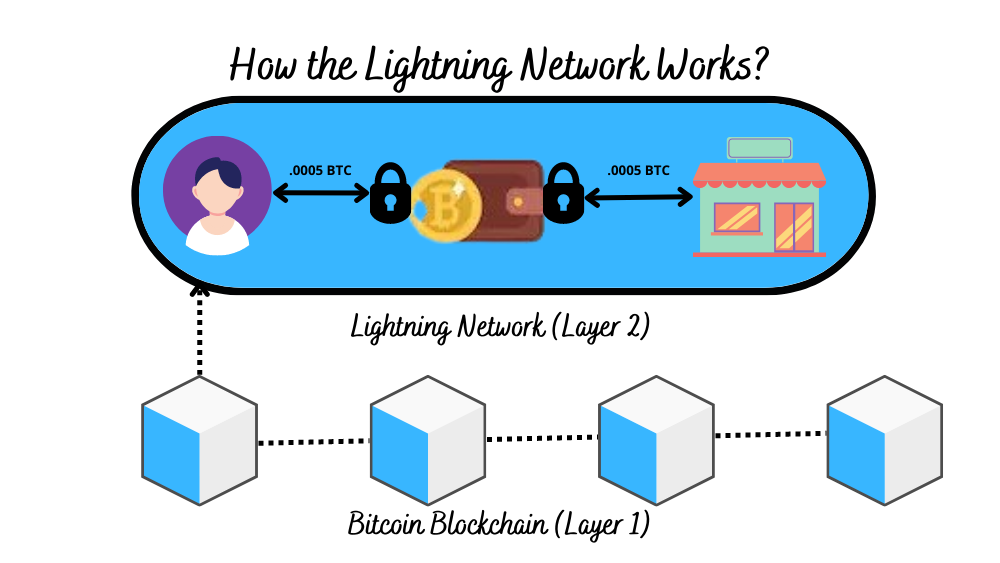
How the Lightning Network Works: A High-Level Overview
The Lightning Network addresses Bitcoin’s scalability issues by enabling users to conduct transactions off-chain, meaning outside the main Bitcoin blockchain. Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works:
- Opening a Channel: Two parties who want to transact frequently with each other can open a payment channel by creating a multi-signature wallet on the Bitcoin blockchain. This wallet requires both parties to agree on any transaction before it can be executed. Both parties deposit an agreed-upon amount of Bitcoin into this wallet.
- Off-Chain Transactions: Once the channel is open, the parties can transact with each other an unlimited number of times without broadcasting each transaction to the Bitcoin blockchain. Each transaction updates the balance within the channel, reflecting the transfer of funds between the parties.
- Closing the Channel: When the parties no longer need to transact with each other, they can close the channel. The final balance of the channel is then recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Technical Details: Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs)
The Lightning Network relies on a technology called Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs) to ensure that transactions are secure and reliable. HTLCs enable conditional payments that are only executed if certain conditions are met within a specific time frame.

Here’s how HTLCs work:
- Hash Lock: The payer generates a secret number and creates a hash of that number. The payer then includes the hash in the payment to the payee.
- Time Lock: The payment is also subject to a time lock, which means that the payee can only claim the payment within a specific time frame.
- Claiming the Payment: To claim the payment, the payee must provide the secret number that was used to create the hash. Once the payer verifies that the secret number matches the hash, the payment is executed.
- Refund: If the payee fails to provide the secret number within the specified time frame, the payment is automatically refunded to the payer.

HTLCs allow payments to be routed through multiple channels in the Lightning Network. If two parties don’t have a direct channel open, they can still transact with each other through a network of interconnected channels. The HTLC ensures that each intermediary in the route is incentivized to forward the payment correctly.
Benefits of the Lightning Network
The Lightning Network offers several significant benefits compared to traditional Bitcoin transactions:
- Faster Transactions: Transactions on the Lightning Network are nearly instantaneous, as they don’t require confirmation on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- Lower Fees: Transaction fees on the Lightning Network are significantly lower than on the Bitcoin blockchain, making it suitable for microtransactions.
- Scalability: The Lightning Network can handle a much larger volume of transactions than the Bitcoin blockchain, enabling it to scale to meet the demands of a global payment system.
- Privacy: Transactions on the Lightning Network are more private than on the Bitcoin blockchain, as they are not publicly recorded.
- Microtransactions: The low fees and fast transaction times make the Lightning Network ideal for microtransactions, opening up new possibilities for use cases such as pay-per-article content, streaming services, and micropayments for online services.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its benefits, the Lightning Network also faces some challenges and limitations:
- Complexity: Setting up and managing Lightning Network channels can be technically challenging for novice users.
- Liquidity: The Lightning Network requires sufficient liquidity in the channels to facilitate transactions. If a channel doesn’t have enough funds, transactions may fail.
- Routing Issues: Finding the optimal route for a payment can be complex, especially in a large and decentralized network.
- Channel Management: Users need to actively manage their channels, ensuring that they have sufficient funds and are properly connected to the network.
- Centralization Concerns: There are concerns that the Lightning Network could become centralized if a few large nodes control a significant portion of the network’s capacity.
The Future of the Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to transform Bitcoin into a viable payment system for everyday transactions. As the network matures, it is likely to become more user-friendly, reliable, and scalable.
Several projects are underway to improve the Lightning Network, including:
- Simplified Channel Management: Developing tools and interfaces that make it easier for users to open, manage, and close channels.
- Improved Routing Algorithms: Developing more efficient routing algorithms that can find the optimal path for payments, even in a large and complex network.
- Increased Liquidity: Incentivizing users to provide liquidity to the network, ensuring that there are sufficient funds available to facilitate transactions.
- Privacy Enhancements: Implementing privacy-enhancing technologies to further protect users’ transaction data.
Conclusion
The Lightning Network is a promising solution to Bitcoin’s scalability challenges. By enabling faster, cheaper, and more private transactions, it has the potential to make Bitcoin a viable payment system for everyday use. While the Lightning Network still faces some challenges, ongoing development efforts are focused on addressing these issues and making the network more user-friendly, reliable, and scalable.
As the Lightning Network matures, it could play a significant role in the future of Bitcoin and the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem. It offers a glimpse into a future where digital currencies can be used seamlessly for a wide range of transactions, from microtransactions to large payments, without the limitations of traditional payment systems.

