- Bitcoin And Blockchain Explained
- Bitcoin Regulation Worldwide: A Shifting Landscape Of Opportunity And Control
- Bitcoin Volatility Explained: Understanding The Wild Ride Of Crypto’s Flagship Asset
- How Meme Coins Are Shaping The Future Of Digital Currency
- Bitcoin Price Prediction 2025: Decoding The Future Of The Crypto King
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, has revolutionized the world of finance and technology. Its decentralized nature, scarcity, and potential for secure transactions have captured the attention of investors, technologists, and individuals seeking alternatives to traditional financial systems. However, understanding Bitcoin can be daunting for newcomers. This comprehensive guide will break down the fundamentals of Bitcoin, making it accessible and understandable for beginners.
What is Bitcoin?
At its core, Bitcoin is a digital currency or cryptocurrency. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat currencies), Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning no single entity controls it. Bitcoin is designed to be:
- Decentralized: No central authority like a bank or government controls Bitcoin.
- Peer-to-Peer: Transactions occur directly between users without intermediaries.
- Limited Supply: There will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins.
- Transparent: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain.
- Secure: Cryptography secures the network and transactions.
The History of Bitcoin
Bitcoin was created in 2008 by an anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. In October 2008, Nakamoto published a whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," outlining the design and principles of Bitcoin. In January 2009, the Bitcoin network was launched, and the first Bitcoin transaction occurred.
Satoshi Nakamoto remained involved in the Bitcoin project for a few years, communicating with developers and contributing to the codebase. However, in 2010, Nakamoto gradually withdrew from the project, leaving the development and maintenance of Bitcoin to the open-source community. The identity of Satoshi Nakamoto remains a mystery to this day.
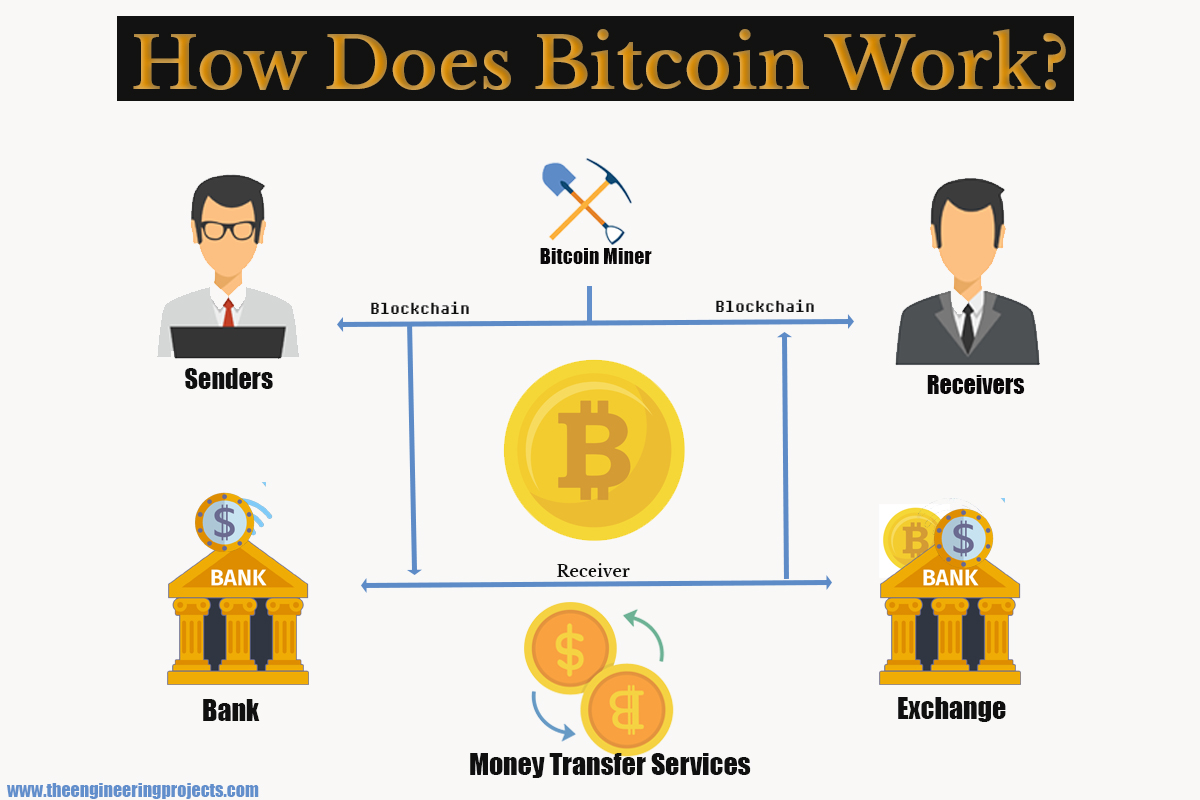
The Blockchain: The Foundation of Bitcoin
The blockchain is the underlying technology that makes Bitcoin possible. It is a public, distributed ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions in a chronological order. Here’s how it works:

-
Transactions: When someone sends Bitcoin to another person, the transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network.

Blocks: Transactions are grouped together into blocks. Each block contains a set of recent transactions, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block in the chain.
-
Mining: Miners are individuals or companies that use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems. When a miner solves the problem, they can add the new block to the blockchain. This process is called mining.
-
Chain: Once a block is added to the blockchain, it becomes a permanent and unalterable part of the chain. Each new block is linked to the previous block, forming a chain of blocks.
-
Consensus: The Bitcoin network uses a consensus mechanism called Proof-of-Work (PoW) to ensure that all participants agree on the validity of the blockchain. PoW requires miners to expend significant computational effort to solve the mathematical problems and add new blocks to the chain.
Key Concepts
- Decentralization: The absence of a central authority is a core principle.
- Cryptography: Cryptography ensures the security and integrity of the network.
- Mining: The process of validating transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain.
- Wallets: Software or hardware that allows you to store, send, and receive Bitcoin.
- Private Keys: Secret codes that allow you to access and control your Bitcoin.
- Public Keys: Addresses that you can share with others to receive Bitcoin.
- Transaction Fees: Small fees paid to miners to incentivize them to process transactions.
- Halving: An event that occurs approximately every four years, reducing the reward for mining new blocks by half.
- Nodes: Computers running Bitcoin software that maintain a copy of the blockchain and help validate transactions.
How to Acquire Bitcoin
- Exchanges: Online platforms where you can buy and sell Bitcoin using fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies.
- Mining: Participate in the process of validating transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain.
- Direct Purchase: Buy Bitcoin directly from individuals who are willing to sell it.
- Earning: Receive Bitcoin as payment for goods or services.
Bitcoin Wallets
A Bitcoin wallet is a software or hardware that allows you to store, send, and receive Bitcoin. There are several types of Bitcoin wallets available:
- Software Wallets: Applications that you can install on your computer or smartphone.
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices that store your private keys offline, providing an extra layer of security.
- Web Wallets: Online services that allow you to access your Bitcoin through a web browser.
- Paper Wallets: Physical documents that contain your public and private keys.
The Benefits of Bitcoin
- Decentralization: Freedom from government or financial institution control.
- Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger.
- Scarcity: Limited supply of 21 million Bitcoins.
- Security: Cryptography secures the network and transactions.
- Lower Fees: Transactions can be cheaper than traditional banking services.
- Global Transactions: Bitcoin can be sent and received anywhere in the world.
- Potential Investment: Bitcoin’s value has increased significantly over time.
The Risks of Bitcoin
- Volatility: Bitcoin’s price can fluctuate significantly.
- Security Risks: Wallets can be hacked, and private keys can be lost or stolen.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal and regulatory status of Bitcoin is still evolving in many countries.
- Scalability Issues: The Bitcoin network can be slow and expensive during periods of high demand.
- Complexity: Understanding Bitcoin and its underlying technology can be challenging for beginners.
Bitcoin Mining Explained
Mining is a crucial aspect of Bitcoin’s functionality. Miners essentially compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain. As a reward, they receive newly minted Bitcoin and transaction fees from the transactions included in the block.
The difficulty of these puzzles is adjusted periodically to maintain a consistent block creation time (approximately every 10 minutes). This adjustment ensures that the rate at which new Bitcoins are created remains predictable.
Transaction Fees
While Bitcoin is often touted as a low-cost alternative to traditional payment systems, transaction fees are still a factor. These fees are paid to miners as an incentive to include your transaction in a block. The higher the fee, the more likely your transaction will be processed quickly.
Transaction fees are typically small, but they can increase during periods of high network congestion. Users can choose the fee they want to pay, but lower fees may result in longer transaction confirmation times.
The Halving Event
The Bitcoin halving is a pre-programmed event that occurs approximately every four years. During a halving, the reward for mining new blocks is reduced by half. This event is designed to control the supply of Bitcoin and maintain its scarcity.
Historically, halvings have been associated with significant price increases in Bitcoin. The reduced supply, coupled with continued demand, can lead to higher prices.
Bitcoin’s Future
The future of Bitcoin is uncertain, but it has the potential to transform the world of finance and technology. Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, scarcity, and potential for secure transactions make it an attractive alternative to traditional financial systems.
However, Bitcoin also faces challenges, including volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and scalability issues. The success of Bitcoin will depend on its ability to overcome these challenges and continue to innovate.
Conclusion
Bitcoin is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to change the world. While it can seem complex at first, understanding the fundamentals is essential for anyone interested in cryptocurrencies or the future of finance. By grasping the concepts outlined in this guide, beginners can gain a solid foundation for exploring the world of Bitcoin and its potential.
Remember to always do your own research and consult with financial professionals before making any investment decisions.

