- Bitcoin’s Role In Decentralization: A Paradigm Shift In Power Dynamics
- Bitcoin Price Prediction 2024: Analyzing Trends, Experts, And Future Potential
- Bitcoin Halving 2025: A Deep Dive Into Potential Impacts And Future Prospects
- Buying Bitcoin With PayPal: A Comprehensive Guide
- How To Store Bitcoin Securely: A Comprehensive Guide
For centuries, fiat currency has reigned supreme as the world’s dominant form of money. However, the advent of Bitcoin in 2009 introduced a revolutionary alternative, challenging the traditional financial system. This article delves into a detailed comparison of Bitcoin and fiat currency, examining their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and potential future roles in the global economy.
Understanding Fiat Currency
Definition and Characteristics
Fiat currency is a legal tender declared by a government to be money. It is not backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver but rather by the government’s creditworthiness and regulatory power. Key characteristics of fiat currency include:
* **Centralized Control:** Issued and regulated by central banks or government entities.
* **Legal Tender Status:** Recognized by law as a valid means of payment within a specific jurisdiction.
* **Unlimited Supply:** Central banks can print more money, potentially leading to inflation.
* **Physical and Digital Forms:** Exists as physical banknotes and coins, as well as digital representations in bank accounts.Advantages of Fiat Currency
* **Stability:** Generally more stable than Bitcoin due to government regulation and monetary policies.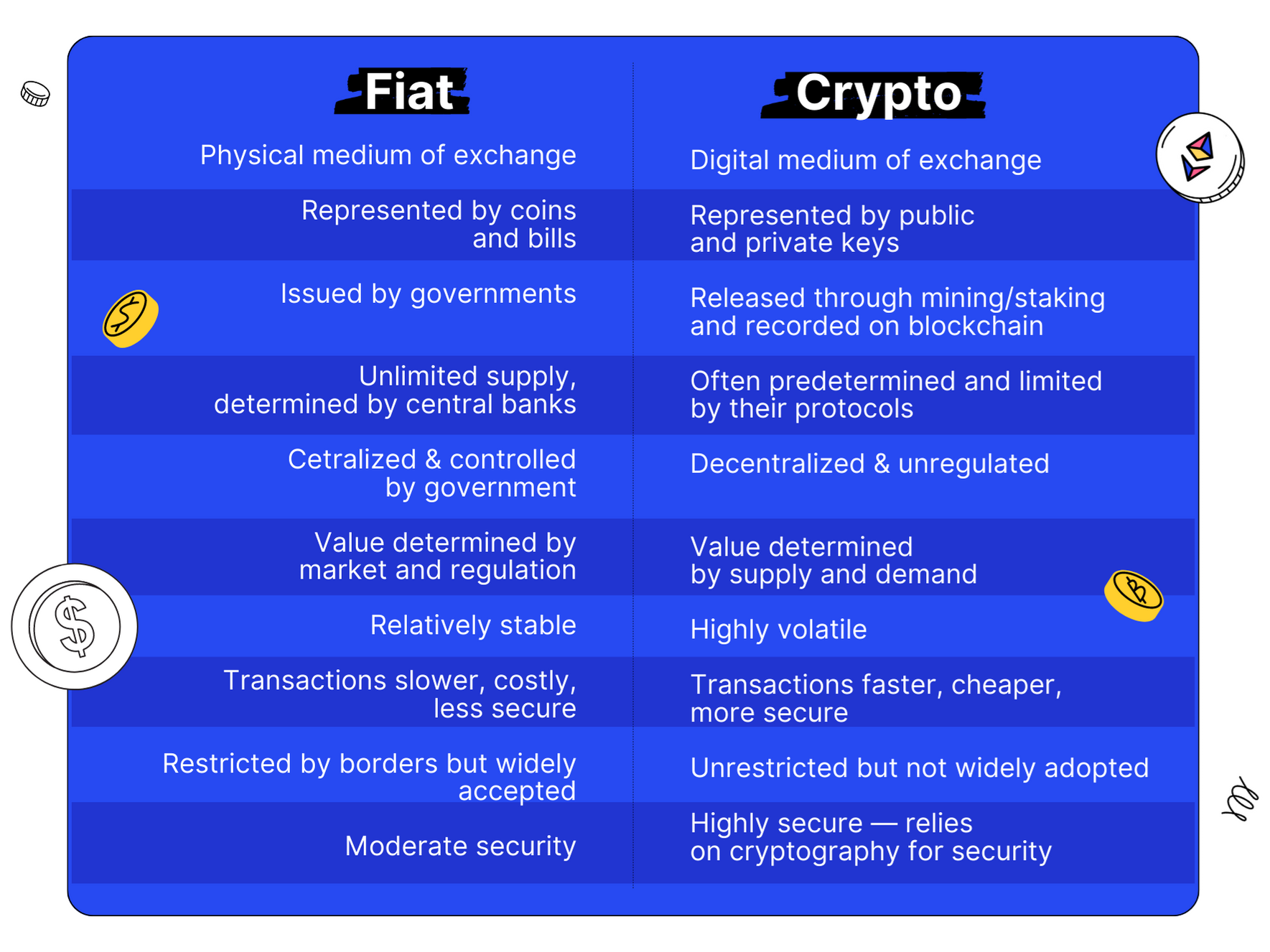 * **Widespread Acceptance:** Universally accepted within its jurisdiction for transactions and payments.
* **Established Infrastructure:** Supported by a well-developed banking system, payment networks, and financial institutions.
* **Government Backing:** Backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government, providing a degree of security.
* **Widespread Acceptance:** Universally accepted within its jurisdiction for transactions and payments.
* **Established Infrastructure:** Supported by a well-developed banking system, payment networks, and financial institutions.
* **Government Backing:** Backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government, providing a degree of security.Disadvantages of Fiat Currency
* **Inflation:** Susceptible to inflation due to the ability of central banks to increase the money supply. * **Centralized Control:** Subject to government manipulation and control, potentially leading to economic instability.
* **Counterfeiting:** Vulnerable to counterfeiting, requiring constant security measures.
* **Transaction Fees:** Often involves transaction fees, especially for international transfers.
* **Lack of Transparency:** Monetary policies and financial decisions are often opaque, lacking public oversight.
* **Centralized Control:** Subject to government manipulation and control, potentially leading to economic instability.
* **Counterfeiting:** Vulnerable to counterfeiting, requiring constant security measures.
* **Transaction Fees:** Often involves transaction fees, especially for international transfers.
* **Lack of Transparency:** Monetary policies and financial decisions are often opaque, lacking public oversight.Understanding Bitcoin

Definition and Characteristics
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency created in 2009 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a technology called blockchain, a distributed ledger that records all transactions in a secure and transparent manner. Key characteristics of Bitcoin include:
* **Decentralization:** Not controlled by any single entity, such as a central bank or government.
* **Limited Supply:** The total number of Bitcoins that can ever be created is capped at 21 million.
* **Cryptography:** Uses cryptography to secure transactions and control the creation of new units.
* **Transparency:** All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent and immutable record.
* **Peer-to-Peer:** Transactions occur directly between users without the need for intermediaries.Advantages of Bitcoin
* **Decentralization:** Eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and increasing efficiency.
* **Limited Supply:** Scarcity can lead to appreciation in value over time, acting as a hedge against inflation.
* **Security:** Cryptography ensures the security and integrity of transactions, making it difficult to counterfeit or manipulate.
* **Transparency:** The blockchain provides a transparent record of all transactions, promoting trust and accountability.
* **Global Accessibility:** Can be used by anyone with an internet connection, regardless of their location or financial status.
* **Lower Transaction Fees:** Often lower than traditional banking fees, especially for international transfers.Disadvantages of Bitcoin
* **Volatility:** Highly volatile, with prices subject to rapid and unpredictable fluctuations.
* **Scalability:** Limited transaction processing capacity, leading to slower transaction times and higher fees during peak periods.
* **Regulatory Uncertainty:** Legal and regulatory status varies across different jurisdictions, creating uncertainty for users and businesses.
* **Complexity:** Can be complex for non-technical users to understand and use safely.
* **Security Risks:** Vulnerable to hacking and theft if not stored securely.
* **Environmental Concerns:** Mining Bitcoin requires significant amounts of energy, raising concerns about its environmental impact.Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | Fiat Currency | Bitcoin |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized (Central Banks/Governments) | Decentralized (No single authority) |
| Supply | Unlimited (Can be printed) | Limited (21 million) |
| Backing | Government Creditworthiness | Cryptography, Network Consensus |
| Stability | Generally More Stable | Highly Volatile |
| Acceptance | Widespread within Jurisdiction | Growing, but not universal |
| Transaction Fees | Can be High (Especially International) | Potentially Lower (But can spike) |
| Transparency | Limited | High (Blockchain) |
| Security | Vulnerable to Counterfeiting | Secure (Cryptography), but risk of theft |
| Inflation | Susceptible to Inflation | Potential Hedge Against Inflation |
| Accessibility | Requires Bank Account | Internet Access Required |
| Regulation | Heavily Regulated | Varies by Jurisdiction, Often Unclear |
Use Cases and Applications
Fiat Currency Use Cases
* **Everyday Transactions:** Purchasing goods and services in local markets.
* **Salaries and Wages:** Receiving income from employers.
* **Paying Taxes:** Fulfilling tax obligations to governments.
* **Savings and Investments:** Storing wealth in bank accounts or investing in traditional assets.
* **International Trade:** Facilitating cross-border transactions between businesses and countries.Bitcoin Use Cases
* **Digital Gold:** Store of value, similar to gold, used to preserve wealth over time.
* **Remittances:** Sending money across borders quickly and cheaply.
* **Online Payments:** Purchasing goods and services online, especially where traditional payment methods are not available.
* **Decentralized Finance (DeFi):** Participating in decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading platforms.
* **Censorship Resistance:** Circumventing censorship and financial restrictions in countries with oppressive regimes.
* **Investment:** Speculative investment in a potentially high-growth asset.The Future of Money
The debate over Bitcoin vs. fiat currency is not necessarily about one replacing the other entirely. Instead, it is more likely that they will coexist in the future, each serving different purposes and catering to different needs.
Potential Scenarios
* **Coexistence:** Fiat currency remains the primary medium of exchange for everyday transactions, while Bitcoin serves as a store of value and a hedge against inflation.
* **Integration:** Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies become more integrated into the traditional financial system, with banks and financial institutions offering Bitcoin-related services.
* **Digital Currencies:** Central banks issue their own digital currencies (CBDCs), competing with both fiat currency and Bitcoin.
* **Hybrid Models:** New financial models emerge that combine the benefits of both fiat currency and Bitcoin, such as stablecoins pegged to fiat currencies.Conclusion
Bitcoin and fiat currency represent fundamentally different approaches to money. Fiat currency is centralized, government-backed, and widely accepted, while Bitcoin is decentralized, scarce, and secured by cryptography. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, and their future roles in the global economy will depend on a variety of factors, including technological advancements, regulatory developments, and societal adoption. As the world becomes increasingly digital, it is essential to understand the characteristics and potential of both Bitcoin and fiat currency to navigate the evolving financial landscape.

