- Bitcoin Mining Profitability: Navigating The Landscape In [Year]
- How Meme Coins Are Shaping The Future Of Digital Currency
- Bitcoin Mining Profitability: A Comprehensive Guide
- Bitcoin Mining: A Comprehensive Guide
- What Is Bitcoin? A Comprehensive Guide To The World’s First Cryptocurrency
Bitcoin, the world’s first and most well-known cryptocurrency, has revolutionized the way we think about digital assets and decentralized finance. However, its energy consumption has become a significant point of contention. The process of Bitcoin mining, which is essential for verifying transactions and securing the network, requires immense computational power, leading to substantial electricity usage. This article delves into the details of Bitcoin’s energy footprint, exploring the factors that influence it, the debates surrounding its environmental impact, and potential solutions for a more sustainable future.
Understanding Bitcoin Mining
To understand the energy consumption of Bitcoin, it’s crucial to first grasp the basics of Bitcoin mining. Bitcoin operates on a decentralized, peer-to-peer network, meaning there is no central authority like a bank to oversee transactions. Instead, a distributed network of computers, known as "miners," performs this role.
Miners use specialized hardware to solve complex cryptographic puzzles. The first miner to solve a puzzle gets to add a new block of transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins and transaction fees. This process is called "proof-of-work" (PoW), and it’s designed to be computationally intensive to prevent malicious actors from easily manipulating the blockchain.
Why Does Bitcoin Mining Consume So Much Energy?
The PoW consensus mechanism is the primary driver of Bitcoin’s energy consumption. Here’s why:
-
Computational Complexity: The cryptographic puzzles miners solve are intentionally difficult. The difficulty is adjusted regularly to maintain a consistent rate of new block creation (approximately every 10 minutes). As more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, requiring more computational power to stay competitive.
-
The Race to Solve: Miners are in a constant race to solve the puzzles first. This competition drives them to use the most powerful and efficient hardware available, leading to an arms race of energy consumption.
-
Specialized Hardware: Bitcoin mining is typically performed using Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs). These are specialized computers designed solely for mining Bitcoin. ASICs are far more efficient than general-purpose computers, but they still consume a significant amount of electricity.

-
Global Network: The Bitcoin network operates 24/7 across the globe. This means that mining operations are constantly running, consuming electricity continuously.

Estimating Bitcoin’s Energy Consumption: A Complex Task
Determining the precise amount of energy Bitcoin mining consumes is challenging due to the decentralized and opaque nature of the network. However, several organizations and researchers have attempted to estimate Bitcoin’s energy usage using various methodologies.
-
Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index (CBECI): Developed by the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance (CCAF), the CBECI is one of the most widely cited sources for estimating Bitcoin’s energy consumption. It uses a model based on the efficiency of mining hardware and network hashrate (the total computational power of the network). The CBECI provides a real-time estimate of Bitcoin’s annualized electricity consumption.
-
Digiconomist Bitcoin Energy Consumption Index: Created by Alex de Vries, this index estimates Bitcoin’s energy consumption based on the minimum electricity required to sustain the Bitcoin network.
How Much Energy Does Bitcoin Actually Use?
Estimates vary, but most sources indicate that Bitcoin’s annual electricity consumption is comparable to that of entire countries. According to the CBECI, Bitcoin’s annualized electricity consumption has fluctuated significantly over time, depending on Bitcoin’s price and the number of miners on the network.
To put this into perspective:
- Bitcoin’s annual electricity consumption is often compared to that of countries like Argentina, Norway, or Ukraine.
- It’s estimated that Bitcoin’s electricity usage is greater than that of Google.
- The carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining is substantial, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
The Environmental Impact of Bitcoin Mining
The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining is a major concern due to its high energy consumption and the sources of electricity used to power mining operations.
-
Carbon Emissions: A significant portion of Bitcoin mining is powered by fossil fuels, particularly coal, especially in regions like China and Kazakhstan, which have historically been major mining hubs. This results in substantial carbon emissions, contributing to climate change.
-
E-Waste: The rapid pace of technological advancement in mining hardware leads to a high turnover of ASICs. These specialized computers become obsolete quickly, generating a large amount of electronic waste (e-waste), which can be harmful to the environment if not properly disposed of.
-
Noise Pollution: Bitcoin mining operations can generate significant noise pollution, particularly when located in residential areas. This can disrupt communities and negatively impact the quality of life for residents.
The Debate Surrounding Bitcoin’s Energy Consumption
The energy consumption of Bitcoin mining has sparked a heated debate, with proponents and critics offering different perspectives.
-
Arguments Against Bitcoin’s Energy Consumption:
- Wasteful Use of Resources: Critics argue that Bitcoin’s energy consumption is a wasteful use of resources, especially when compared to traditional financial systems or other cryptocurrencies that use more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms.
- Environmental Damage: The environmental impact of Bitcoin mining, including carbon emissions and e-waste, is a major concern for environmentalists and policymakers.
- Opportunity Cost: The electricity used for Bitcoin mining could be used for other, more beneficial purposes, such as powering homes, businesses, or public services.
-
Arguments in Favor of Bitcoin’s Energy Consumption:
- Decentralization and Security: Proponents argue that the energy-intensive PoW consensus mechanism is necessary to maintain the decentralization and security of the Bitcoin network.
- Economic Benefits: Bitcoin mining can provide economic benefits to regions with abundant and cheap electricity, creating jobs and stimulating economic growth.
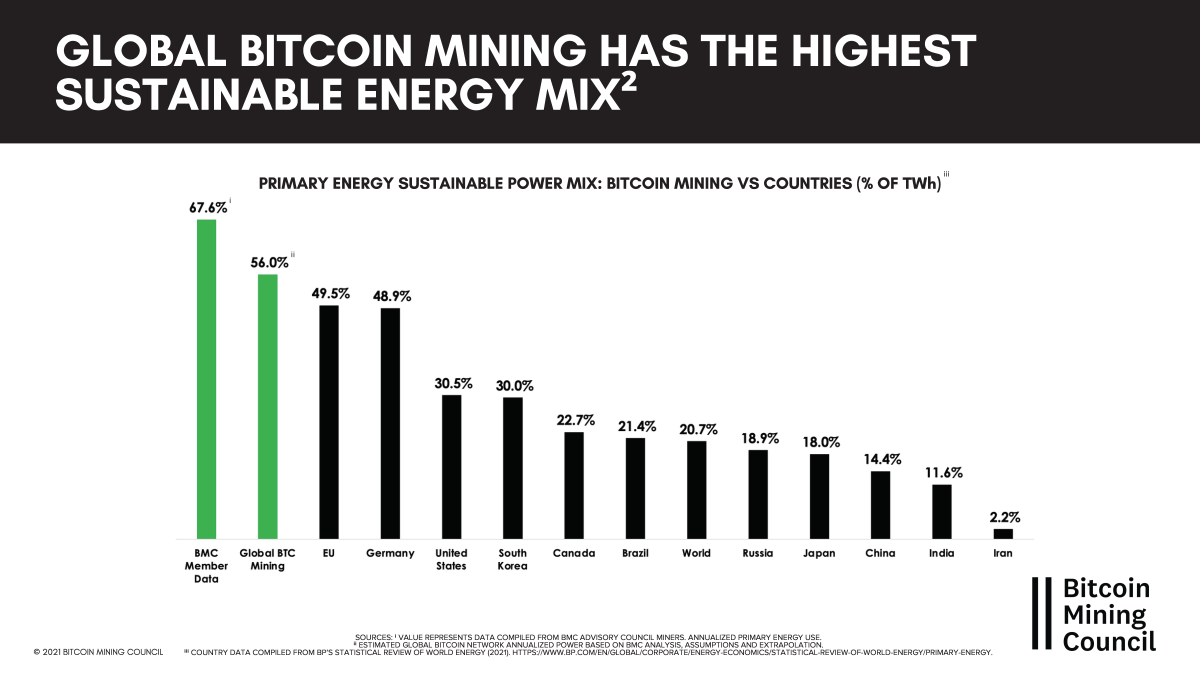
- Renewable Energy Use: Some miners are increasingly using renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro, to power their operations, reducing the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining.
- Innovation and Efficiency: The Bitcoin mining industry is constantly innovating to improve energy efficiency and reduce its environmental footprint.
Potential Solutions for a More Sustainable Bitcoin
Addressing the energy consumption of Bitcoin mining requires a multi-faceted approach that involves technological innovation, policy changes, and industry collaboration.
-
Transition to Renewable Energy: Encouraging miners to use renewable energy sources is a key step towards reducing Bitcoin’s carbon footprint. This can be achieved through incentives, regulations, and public awareness campaigns.
-
Energy Efficiency Improvements: Developing more energy-efficient mining hardware and software can significantly reduce the amount of electricity required to mine Bitcoin.
-
Alternative Consensus Mechanisms: Exploring and adopting alternative consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS), which require far less energy than PoW, could be a game-changer. Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency, has already transitioned to PoS, reducing its energy consumption by over 99%.
-
Carbon Offsetting: Miners can offset their carbon emissions by investing in carbon reduction projects, such as reforestation or renewable energy development.
-
Regulation and Standards: Governments and industry organizations can establish regulations and standards for Bitcoin mining, promoting sustainable practices and reducing environmental impact.
The Future of Bitcoin Mining and Energy Consumption
The future of Bitcoin mining and its energy consumption is uncertain, but several trends and developments are likely to shape its trajectory.
- Increased Adoption of Renewable Energy: As renewable energy becomes more affordable and accessible, more miners are likely to transition to using it to power their operations.
- Geographic Shifts in Mining Operations: Mining operations may shift to regions with abundant and cheap renewable energy, such as Iceland or Norway.
- Technological Innovations: Continued innovation in mining hardware and software will likely lead to further improvements in energy efficiency.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Governments and regulatory bodies are likely to increase their scrutiny of Bitcoin mining and its environmental impact, potentially leading to stricter regulations.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s energy consumption is a complex and controversial issue. While the PoW consensus mechanism provides security and decentralization, it also leads to significant electricity usage and environmental impact. Addressing this challenge requires a concerted effort from miners, developers, policymakers, and the broader Bitcoin community. By transitioning to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, exploring alternative consensus mechanisms, and implementing responsible regulations, it is possible to create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly Bitcoin ecosystem. The future of Bitcoin hinges, in part, on its ability to address its energy consumption and demonstrate its commitment to a greener future.

