- Bitcoin Investment Strategies: Navigating The World Of Digital Gold
- How To Buy Bitcoin: A Comprehensive Guide For Beginners And Beyond
- Bitcoin And Blockchain Explained
- What Are Meme Coins And Why Are They So Popular?
- What Is Bitcoin? A Comprehensive Guide To The World’s First Cryptocurrency
Inflation, the silent thief that erodes purchasing power, has been a persistent concern for individuals and economies alike. As traditional assets like stocks and bonds sometimes struggle to maintain their value in inflationary environments, investors are increasingly seeking alternative hedges. Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has emerged as a prominent contender in this space, sparking intense debate about its potential as an inflation hedge. This article delves into the intricate relationship between Bitcoin and inflation, exploring the arguments for and against its role as a safe haven asset.
Understanding Inflation and Its Impact
Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. This means that each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services, effectively reducing the purchasing power of money. Inflation can arise from various factors, including increased demand (demand-pull inflation), rising production costs (cost-push inflation), and expansionary monetary policies by central banks.
The consequences of inflation can be far-reaching. High inflation can erode savings, distort investment decisions, and create economic uncertainty. It can also disproportionately affect low-income individuals and those on fixed incomes, as their purchasing power diminishes. Central banks typically aim to maintain a stable inflation rate, often around 2%, to foster economic stability and sustainable growth.
Bitcoin: A Digital Asset with a Fixed Supply
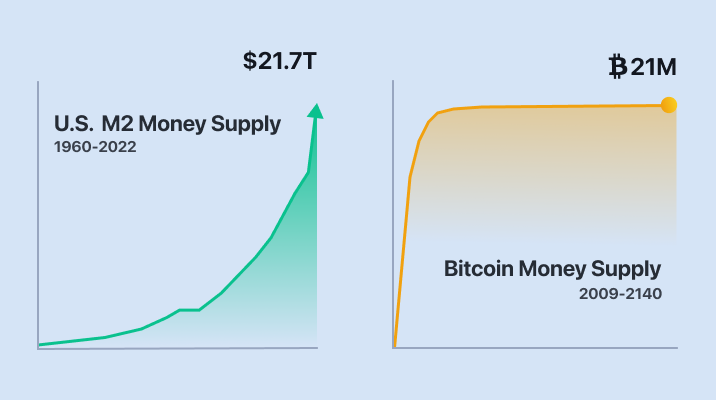
Bitcoin, created in 2009 by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, is a decentralized digital currency that operates on a technology called blockchain. Unlike traditional currencies issued by central banks, Bitcoin has a predetermined and limited supply of 21 million coins. This scarcity is a key feature that proponents believe makes it an attractive hedge against inflation.
The Argument for Bitcoin as an Inflation Hedge
The core argument for Bitcoin as an inflation hedge rests on its limited supply. Traditional fiat currencies can be printed by central banks at will, potentially leading to inflation if the money supply grows faster than the economy’s output. Bitcoin’s fixed supply, on the other hand, ensures that its value cannot be diluted by increasing its quantity.
Here are some key points supporting Bitcoin as an inflation hedge:
- Scarcity: The limited supply of 21 million Bitcoins is a fundamental characteristic that distinguishes it from fiat currencies. This scarcity is often compared to precious metals like gold, which have historically served as stores of value and inflation hedges.
- Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning it is not controlled by any single entity, such as a government or central bank. This decentralization makes it less susceptible to manipulation and political influence, which can contribute to inflation.
- Accessibility: Bitcoin is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, making it a potential store of value for individuals in countries with unstable currencies or high inflation rates.
- Growing Adoption: As Bitcoin gains wider acceptance and adoption, its network effect strengthens, potentially increasing its value and resilience against inflation.

The Counterarguments: Volatility and Other Concerns
Despite the compelling arguments for Bitcoin as an inflation hedge, several counterarguments and concerns need to be considered:
- Volatility: Bitcoin is known for its extreme price volatility. Its price can fluctuate dramatically in short periods, making it a risky asset for those seeking a stable store of value.
- Lack of Intrinsic Value: Unlike traditional assets like stocks or real estate, Bitcoin does not generate cash flow or have underlying assets backing it. Its value is primarily based on speculation and market sentiment.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape surrounding Bitcoin is still evolving, and governments could potentially impose restrictions or bans that negatively impact its value.
- Competition from Other Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin faces competition from thousands of other cryptocurrencies, some of which may offer superior technology or features. This competition could potentially dilute Bitcoin’s dominance and impact its value.
- Energy Consumption: Bitcoin mining, the process of verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain, consumes a significant amount of energy. This has raised environmental concerns and could lead to increased regulatory scrutiny.
- Market Maturity: Bitcoin is still a relatively new asset class, and its long-term performance as an inflation hedge remains uncertain. It has not been tested during prolonged periods of high inflation or economic turmoil.

Empirical Evidence: A Mixed Bag
The empirical evidence on Bitcoin’s effectiveness as an inflation hedge is mixed and inconclusive. Some studies have found a positive correlation between Bitcoin and inflation, suggesting that it can act as a hedge. However, other studies have found no significant relationship or even a negative correlation.
One of the challenges in analyzing Bitcoin’s performance as an inflation hedge is its relatively short history. Bitcoin has only been around for a little over a decade, which is a limited time frame for assessing its long-term effectiveness as a store of value.
Additionally, the macroeconomic environment during Bitcoin’s existence has been characterized by relatively low inflation rates in most developed countries. This makes it difficult to determine how Bitcoin would perform during periods of high inflation.
Bitcoin vs. Gold: A Comparison
Gold has historically been considered a safe haven asset and an inflation hedge. It is often compared to Bitcoin due to its limited supply and perceived store of value. Here’s a comparison of the two:
- Scarcity: Both Bitcoin and gold have limited supplies. However, Bitcoin’s supply is fixed at 21 million coins, while the amount of gold that can be mined is finite but not precisely known.
- History: Gold has a long history as a store of value, dating back thousands of years. Bitcoin, on the other hand, is a relatively new asset class with a limited track record.
- Volatility: Bitcoin is significantly more volatile than gold. Gold’s price tends to be more stable, making it a more reliable store of value for risk-averse investors.
- Accessibility: Bitcoin is more accessible than gold, as it can be easily purchased and stored digitally. Gold, on the other hand, requires physical storage and can be more difficult to trade.
- Use Cases: Gold has various industrial and jewelry applications, while Bitcoin’s primary use case is as a digital currency and store of value.
The Future of Bitcoin and Inflation
The debate over Bitcoin’s role as an inflation hedge is likely to continue as the cryptocurrency market matures and the macroeconomic environment evolves. Whether Bitcoin can truly serve as a reliable store of value during periods of high inflation remains to be seen.
Several factors could influence Bitcoin’s future performance as an inflation hedge:
- Adoption: Increased adoption by institutional investors and mainstream users could strengthen Bitcoin’s network effect and increase its value.
- Regulation: Clear and consistent regulations could provide more certainty and legitimacy to the Bitcoin market, attracting more investors.
- Technological Developments: Improvements in Bitcoin’s technology, such as scalability and energy efficiency, could enhance its appeal and usability.
- Macroeconomic Conditions: High inflation rates and economic uncertainty could drive more investors to seek alternative assets like Bitcoin.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s potential as an inflation hedge is a complex and multifaceted issue. While its limited supply and decentralized nature make it an attractive alternative to traditional fiat currencies, its volatility, lack of intrinsic value, and regulatory uncertainty raise concerns. The empirical evidence on Bitcoin’s effectiveness as an inflation hedge is mixed, and its long-term performance remains uncertain.
Investors considering Bitcoin as an inflation hedge should carefully weigh the risks and potential rewards. It is essential to conduct thorough research, understand the cryptocurrency market, and diversify their portfolios. Bitcoin may offer some protection against inflation, but it is not a guaranteed solution and should be approached with caution.
Ultimately, whether Bitcoin becomes a true safe haven asset will depend on its ability to maintain its value during periods of economic turmoil and high inflation, as well as its continued adoption and acceptance by the broader financial community.

